Introduction to INNER JOIN in PostgreSQL
In PostgreSQL, the INNER JOIN clause is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. It returns a result set containing only the matched rows from both tables. The basic syntax for an INNER JOIN is:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column = table2.column;
The ON clause specifies the condition for matching rows between the tables.
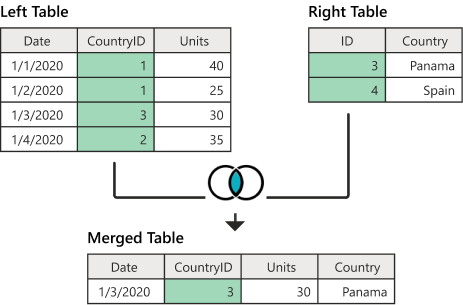
INNER JOIN Diagram
Here's a diagram illustrating how an INNER JOIN works:
Table A Table B
+----------+ +----------+
| id | name | | id | age |
+----+------+ +----+-----+
| 1 | John | | 1 | 25 |
| 2 | Jane | | 2 | 30 |
| 3 | Bob | | 3 | 35 |
+----------+ +----------+
INNER JOIN
+----------+----------+-----+
| Table A.id | Table A.name | Table B.age |
+------------+-------------+-------------+
| 1 | John | 25 |
| 2 | Jane | 30 |
+----------+----------+-----+
The INNER JOIN matches rows from both tables where the specified condition is true, in this case, where table1.column = table2.column. The resulting table contains only the matched rows.
Examples of INNER JOIN
Let's look at some examples of using INNER JOIN in PostgreSQL:
-- Join the employees and departments tables
SELECT employees.first_name, employees.last_name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
This query joins the employees and departments tables based on the department_id column.
-- Join the orders and customers tables with a condition
SELECT orders.order_date, customers.customer_name, orders.total_amount
FROM orders
INNER JOIN customers
ON orders.customer_id = customers.customer_id
WHERE orders.total_amount > 1000;
This query joins the orders and customers tables based on the customer_id column and includes an additional condition to filter orders with a total_amount greater than 1000.
Use Cases for INNER JOIN
INNER JOIN is useful in a variety of scenarios, such as:
-
Combining related data from multiple tables: INNER JOIN allows you to combine data from multiple tables based on a common column, providing a more complete and comprehensive view of the data.
-
Performing complex queries: By joining tables, you can create more complex queries that involve data from multiple sources, enabling more sophisticated analysis and reporting.
-
Enforcing data integrity: INNER JOIN can help ensure data integrity by only returning rows that have matching values in both tables, preventing the inclusion of incomplete or inconsistent data.
-
Optimizing database performance: When used correctly, INNER JOIN can help optimize database performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be processed and returned.
-
Implementing business rules: INNER JOIN can be used to implement business rules that depend on data from multiple tables, such as calculating commissions based on sales and employee data.
Conclusion
INNER JOIN is a powerful tool for combining data from multiple tables in PostgreSQL. By matching rows based on a common column, INNER JOIN allows you to create more comprehensive and meaningful queries. Practice using INNER JOIN in your queries to become more comfortable with its syntax and use cases.
[Pic Credit Microsoft https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Flearn.microsoft.com%2Fen-us%2Fpower-query%2Fmerge-queries-inner&psig=AOvVaw3Jop3SOdE-oNpTbcZsv0vO&ust=1716308690824000&source=images&cd=vfe&opi=89978449&ved=0CBIQjRxqFwoTCPCWvKbSnIYDFQAAAAAdAAAAABAE]